How to find Surface area of 3D objects?
It is the process of finding the area of 3D objects. Firstly all the faces of a 3D object are identified and then their areas are found and added.
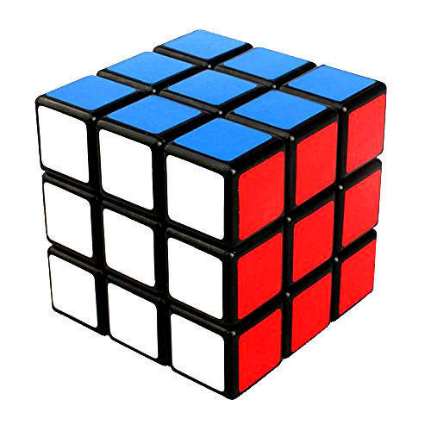
Let’s examine the Rubik's cube. How many faces does it have?
The shape is a cube which is similar to a room with all faces as squares. There are six faces. The blue face is the top face, red is the right side face and the front is indicated in white. If each square in one face is equal to a unit square, there are 9 squares in one face so the area of each face = 9 square units. There are 6 such faces so the total number of squares=9 x 6=54 square units. That is the total surface area of this cube. Now let's examine the following object.
What are polyhedra?
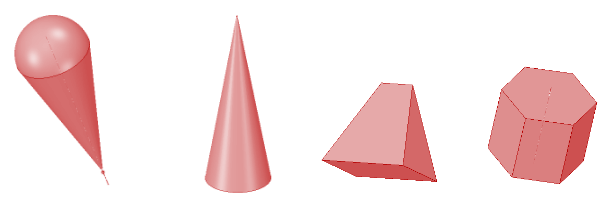
A 3D object that is composed of flat faces only is a polyhedron. Let's have a look at the following figures.
The first figure is composed of curved surfaces only. The second figure is a cone that has one flat face that is a circle and another conical curved surface. The third figure is a triangular prism that has 3 rectangles and two triangles. The fourth figure is a hexagonal prism that has 2 hexagons and 6 rectangles.
Out of the given objects, the last two are polyhedra because they have flat surfaces only.
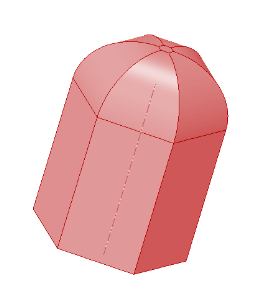
Lets look at the figure below. Is it a polyhedron?
No, because the flat faces are curved at the upper portion of the object.