Important characteristics of cartesian plane
A cartesian plane is a plane with perpendicular axes as described before as shown below. The two horizontal and vertical lines in the plane are x and y axes respectively. The intersection point is the origin and its coordinates (0, 0). The axes divide the plane into four divisions known as quadrants. The quadrants are named 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th.
Plotting a coordinate and the plane
Even though the directions are finalized as horizontal and vertical, there are two options in each direction. While in a horizontal direction a point can lie either on the left side or the right side. Similarly, a point can lie upwards or downwards in the vertical direction. For convention, the points on the left of the origin are taken as negative and on the right are taken as positive. Similarly, the upwards direction is positive and the downwards is negative.
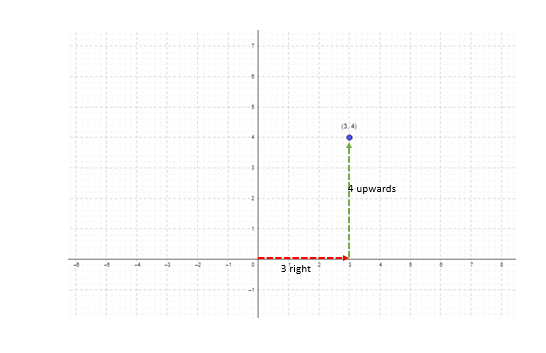
A point denoted (3, 4) lies 3 units to the right and 4 units upwards of the origin. The quadrant in which it lies is the 1st quadrant.
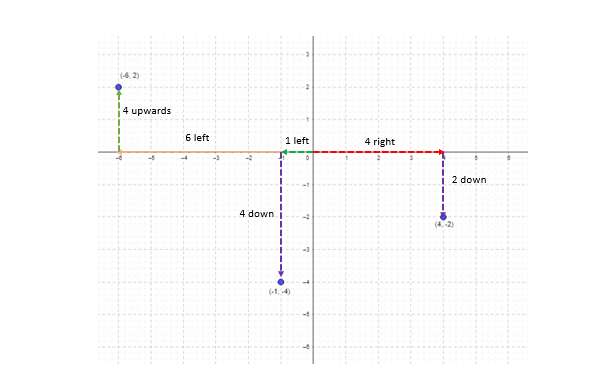
(-6, 2) lies 6 units to the left and 2 units upwards of the origin. (-1, -4) lies 1 unit to the left and 4 units downwards of origin. (4, -2) lies 4 units right and 2 units downwards of origin.
(-6, 2) lies in the 2nd quadrant, (4, -2) in the 4th quadrant, and (-1, -4) in the 3rd quadrant.