Difference between prism and pyramid
Types of polyhedra and their differences
Polyhedra are of two types. The third and fourth objects in the list are of the same types. Let’s observe two polyhedra that are made from the same base.
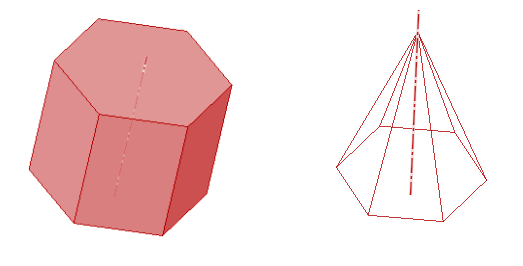
In the figure on the left, 6 rectangles join 2 hexagons whereas the object on the right has six triangles along with one hexagon. The object on the left is a prism while the other is a pyramid. The cross-sectional shape is defined as the shape obtained by slicing a 3D object with a plane parallel to the base (hexagon here). In both cases, the cross-section is of hexagon shape but while the prism has the same size hexagon throughout the shape, the pyramid has its hexagon shape decreasing with increasing height. The rectangular face is predominantly found in prisms whereas triangular faces are prevalent in pyramids.
The cross-sectional area of prism and pyramid
Let's observe a similar case with rectangular base objects.
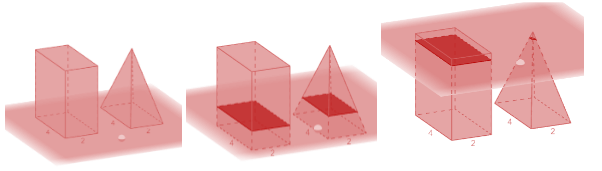
The surface area of polyhedra is often determined with the help of a net diagram. A net diagram of a particular 3D object is a diagram that lays all of its exposed surfaces flat out on the same paper.
Given example below is a net diagram of a hexagonal-based prism.
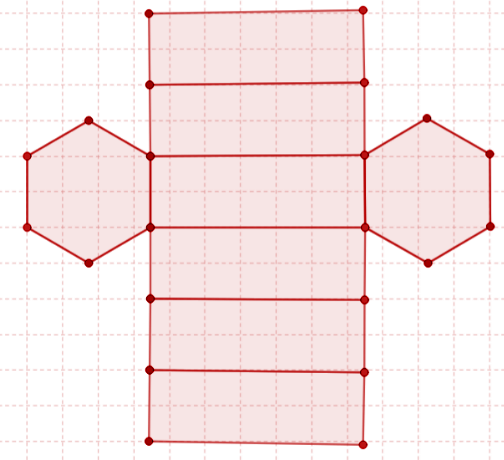
What can be noticed here is that when the given faces are folded then a hexagonal prism is obtained. What is different about the figure below? Does this net diagram also belong to a hexagonal prism?
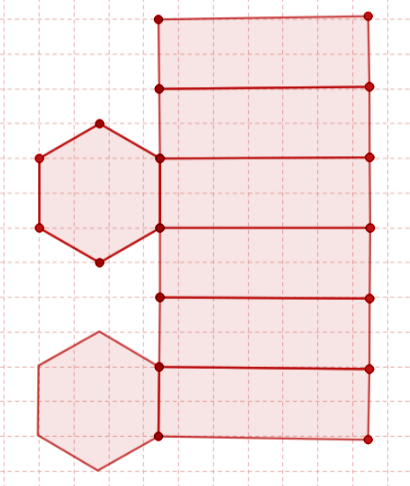
The answer is No, the simple reason being that the hexagons will overlap each other when folded. Both the hexagons are on the same side. The number of faces that we can count on a 3D object by observing it from different angles is shown as normal views in a net diagram. If the diagram contains rectangles then the number of rectangles must be equal to the number of sides in the other two faces (other than a rectangle) each. Those two faces are called bases. In the above diagram, there are 6 rectangles, which means that the available shape of the base in that diagram must be 6-sided or a hexagon. Also, another factor worth considering is that the side of the hexagon must be the same as the rectangle's width.
The same applies to a pyramid but in place of rectangles, there are triangles and in place of one base, there are two bases.
The line formed by the intersection of two faces in a 3D object is called an edge; the point where two edges meet is called a vertex. How many vertices, edges and faces does the figure below contain?
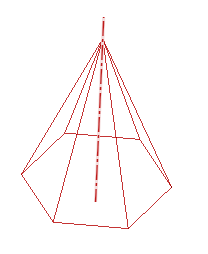
The figure contains 6 triangular faces and one hexagonal base. There are 12 edges and 7 vertices.
